Othman Oudghiri-Idrissi and his collaborators from the NASA Ames Research Center and the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, have received the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) Award. This prestigious award is given by NASA to visionary and innovative ideas that have the potential to transform the future of space exploration and technology.
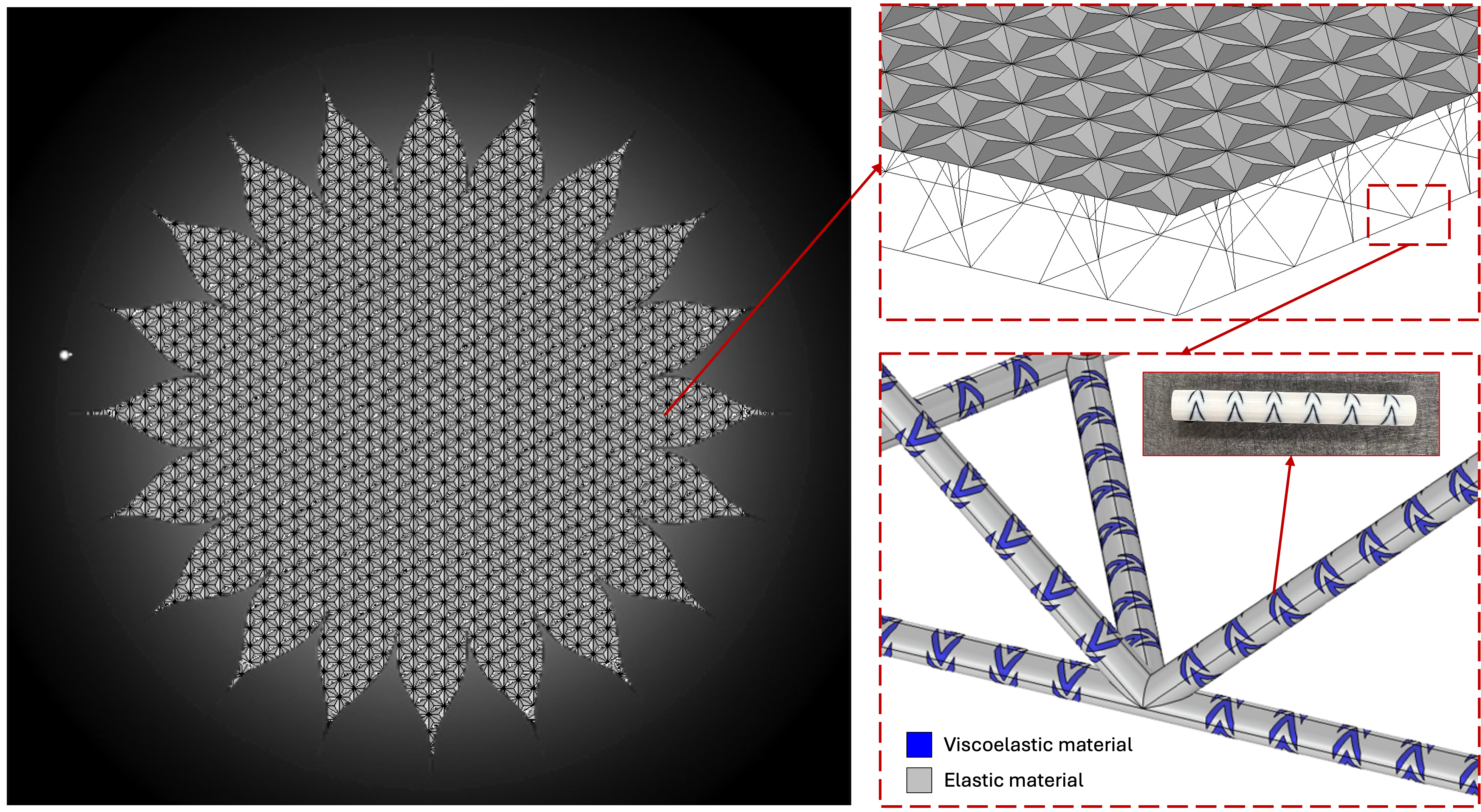
Oudghiri-Idrissi’s winning project, “Dynamically Stable Large Space Structures via Architected Metamaterials,” focuses on advancing the dynamic precision of Starshade—a space occulter designed for exoplanet discovery and observation. This innovative research aims to leverage mechanical metamaterials, such as phononic crystals and viscoelastic metamaterials, to improve the structural stability and performance of large space structures.

The NIAC program is one of NASA's most prestigious awards, recognizing cutting-edge concepts that push the boundaries of current technology and science. Oudghiri-Idrissi’s project exemplifies the program's mission by combining expertise in engineering, physics, and advanced materials to address the challenges of next-generation in-space manufacturable structures.
“This recognition is a testament to the transformative potential of mechanical metamaterials and in-space assembly and manufacturing (ISAM) research,” said Oudghiri-Idrissi. “Our team is committed to advancing metamaterial technologies for space structures and contributing to NASA’s mission of unveiling the secrets of the universe.”
In collaboration with Christine Gregg, Dan Sirbu and Alan Cassel from the NASA Ames Research Center, as well as Serife Tol and Ellen Arruda from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, this project represents a significant step forward in space technology. The team’s work could pave the way to more precise and efficient exoplanet discovery technologies, leading to invaluable insights into worlds beyond our solar system.
Oudghiri-Idrissi’s expertise in architected metamaterials and his dedication to innovative solutions continue to position him as a leader in his field.
For more information on the 2025 NIAC Phase I awardees and this groundbreaking project, visit NASA’s announcement and the project description.







