Slide 10 of 19
Notes:
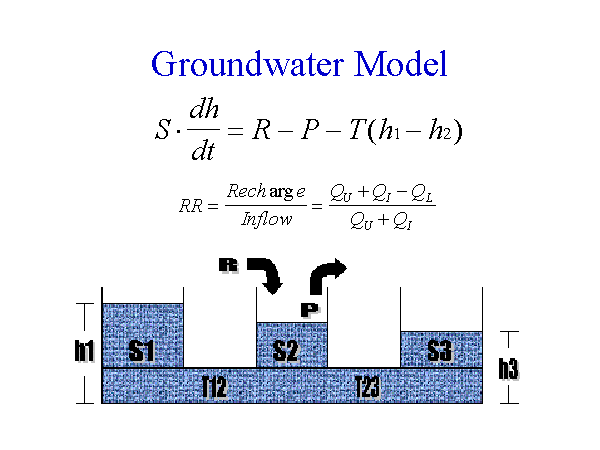
The groundwater model is a lumped-parameter type
- Portions of the formation fed by different catchment areas are assumed� to have uniform storage and transmissivity parameters
- Properties are also averaged over depth
- This is different from finite element models like MODFLOW or GMS� where there is an analysis grid consisting of a large number of cells
- Simulate interaction between surface water and groundwater
- Recharge to aquifer is mostly from channel losses in streams that � flow over outcrop
- Empirical functions were developed by plotting inflows against known� recharge determined by USGS
- Inflow is the stream flow at a gauge above the recharge zone plus� intervening runoff; intervening runoff is calculated using an areal� scaling ratio assuming that conditions are the same for catchment� and intervening regions
Used historical pumping data